This article explores the risks involved in ammonia release and shows how the bowtie method can be used to identify potential causes, strengthen barriers, and reduce the impact of an ammonia release. The industrial use of ammonia (NH₃) is widespread, including chemical manufacturing, fertiliser production, industrial refrigeration, food processing, cold storage logistics, pulp and paper, mining, and semiconductor fabrication. In these sectors, ammonia is often used as a coolant, cleaning agent or part of chemical processing. Despite its versatility, ammonia is a highly reactive and potentially hazardous substance that, if released, can have serious consequences for human safety, plant integrity, and the environment.

Gas containers attached to a control system
Understanding how such risks develop, and how companies can systematically identify and mitigate, is key to building safer operations. Tools like Presight OpenRisk can help visualise critical barriers and improve preparedness before incidents occur.
A well-known ammonia release incident is the 2013 Chinese poultry plant fire at the Jilin Baoyuanfeng Poultry Company, which tragically claimed the lives of 119 workers. Industries commonly use ammonia as a refrigerant in meat packing, poultry, and other food-processing industries, which is associated with frequent leaks and safety incidents. However, none have matched the scale and severity of this disaster. The bowtie method could help visualise the pathway from hazard to a major accident like this one. This accident highlights the serious risks that inadequate safety measures in ammonia-handling operations create.
Properties and Hazard Potential
Ammonia is a colourless gas with a pungent odour and high volatility at ambient temperatures. It is highly soluble in water and forms flammable mixtures with air at certain concentrations. Even at relatively low concentrations, ammonia can irritate the eyes and respiratory system, while higher concentrations may be life-threatening. In enclosed spaces, an ammonia release can cause explosion or suffocation.
Causes of Potential Ammonia Release
Unintentional releases of ammonia can result from a range of factors, typically grouped into technical, organisational, and human factors:
- Technical failures: material fatigue, corrosion, defective seals, leaks in valves or piping
- Operational errors: mishandling during loading or unloading, inadequately trained personnel
- Maintenance issues: missed inspections, lack of condition monitoring
- External impacts: mechanical damage, e.g., from vehicle collisions
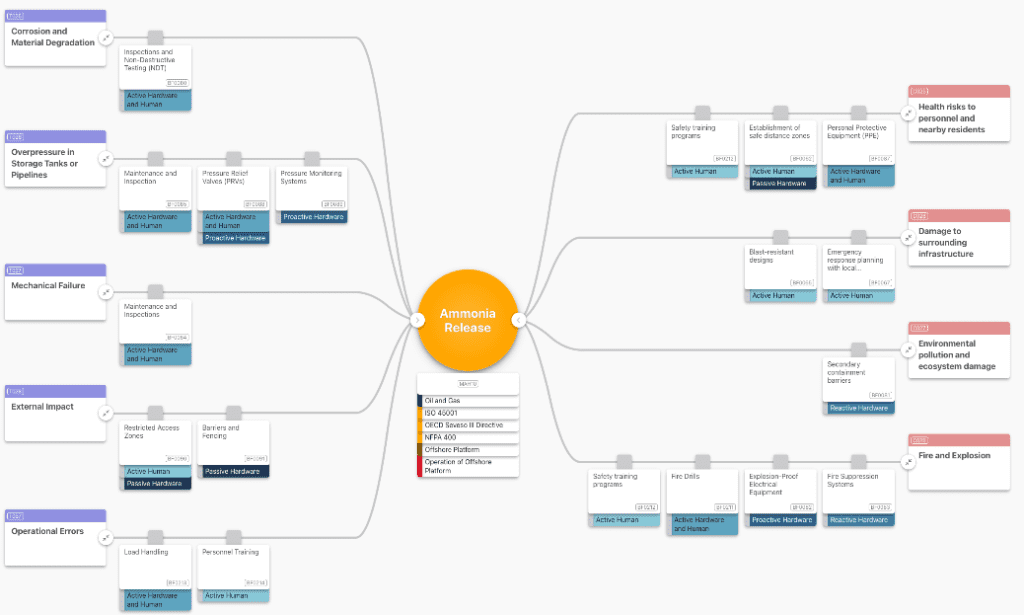
Bowtie diagram showing Ammonia release as the top event. Barriers include info labels to provide more detail. Click here to explore the bowtie: Ammonia Release Bowtie – OpenRisk
Safety Strategies and Risk Analyses using bowtie model
Companies employ established risk management methods to systematically assess the risks associated with ammonia releases and identify both preventive and mitigative measures. One such method is the bowtie analysis, which is particularly suited to scenarios with clearly defined top events, such as ammonia release incidents or other loss of containment accidents. This method provides a structured representation of potential causes (“threats”), consequences, and the preventative and mitigating barriers in place between them. A comprehensive risk assessment should always be multidisciplinary, involving process engineering, occupational safety, maintenance, emergency response, and environmental protection. Tools, such as Presight OpenRisk, can support the structured identification and visualisation of risks.
The release of ammonia represents a complex, interdisciplinary risk that must be addressed both technically and organisationally. Beyond selecting suitable materials, monitoring systems, and protective technologies, integrated risk management is essential to prevent or mitigate potential releases. Applying established analytical methods and leveraging digital tools strengthens safety culture and enhances operational resilience.
For more control over your Process safety and Barrier Management strategy, you can implement Presight Barrier Management allowing you to ensure compliance, and a proactive approach. You can monitor the health of your barriers as part of your process safety strategy. This gives you a full overview of both human factors and technical elements. With Presight Barrier Management you can confidently demonstrate that your assets are safe and that you know it.